Create articles from any YouTube video or use our API to get YouTube transcriptions
Start for freeMilton Friedman's Hypothetical Stance on Donald Trump and the 2024 Election
If Milton Friedman were alive today, his perspective on Donald Trump's potential 2024 presidential win and the current political climate would likely be nuanced and complex. As a renowned economist and champion of free-market principles, Friedman's views would undoubtedly be shaped by his long-standing economic philosophies.
Friedman's Potential Concerns
Friedman would likely express significant reservations about several aspects of Trump's economic policies:
-
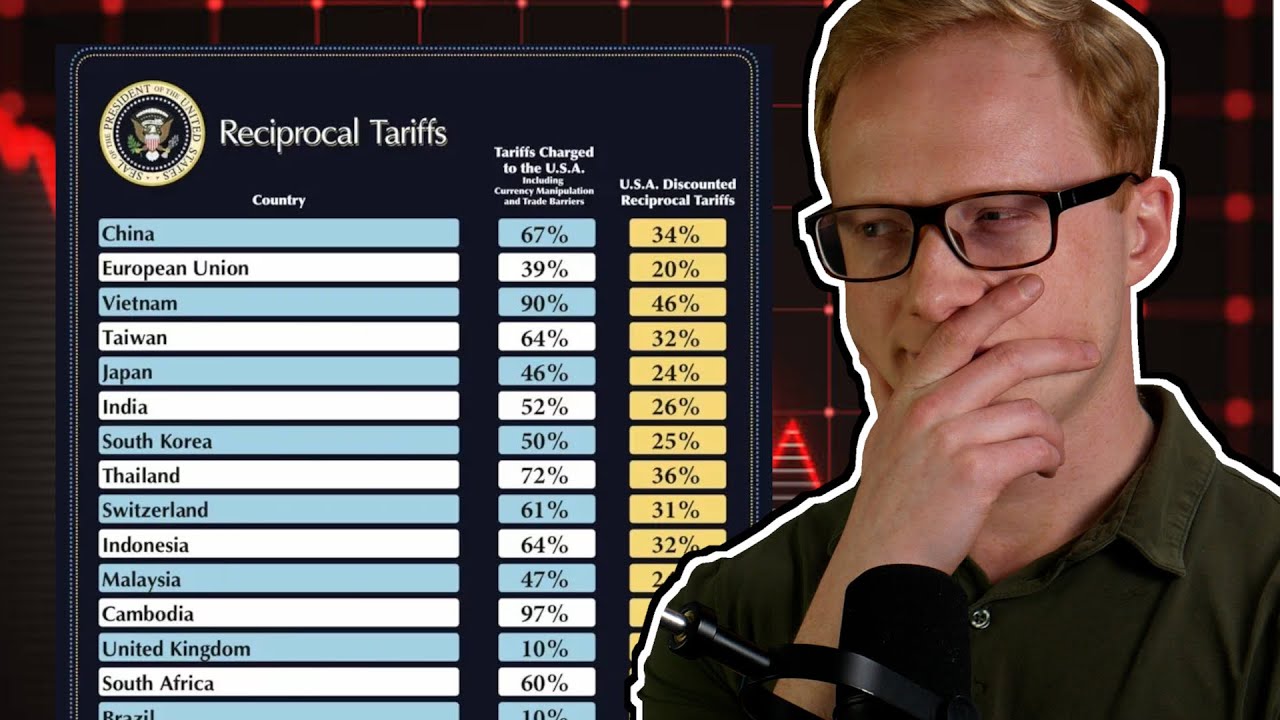
Protectionism and Tariffs: Friedman was a staunch advocate for free trade. He would likely be deeply troubled by Trump's protectionist policies and the imposition of tariffs. Friedman believed that international trade was crucial for maintaining global peace and prosperity.
-
Restrictions on Capital Movement: The economist would probably oppose limitations on foreign investments, such as restrictions on companies like Nippon Steel investing in the United States. Friedman championed the free movement of capital across borders.
-
Fiscal Policy: While Friedman might appreciate efforts to reduce government size, he would likely criticize the Trump administration's spending plans as not fiscally conservative. Friedman was concerned about unchecked government growth rather than deficits per se.
-
Monetary Policy: Friedman would likely be worried about threats to the U.S. dollar's status as the world's reserve currency, especially given increased levels of debt and spending.
-
Interest Rates: Before his passing, Friedman expressed concern about persistently low interest rates. He believed there should be a meaningful price on capital, and excessively low rates could distort economic signals.
Potential Areas of Agreement
Despite these concerns, there might be some areas where Friedman could find common ground with Trump's policies:
-
Deregulation: Friedman was a proponent of reducing government regulation in many sectors. He might approve of some of Trump's deregulatory efforts.
-
Tax Cuts: As an advocate for lower taxes, Friedman might support some aspects of Trump's tax policies, though he would likely prefer them to be accompanied by spending cuts.
-
School Choice: Friedman was a strong proponent of school vouchers and educational choice. He might appreciate any efforts by the Trump administration to expand school choice programs.
The Role of Inflation in Shaping Political Landscapes
One of the most significant economic factors influencing current political dynamics is inflation. The essay "How Inflation Ended Neoliberalism and Reelected Trump" provides valuable insights into this phenomenon.
The Neoliberal Era and Inflation
The neoliberal era, characterized by a focus on monetary policy, free trade, and deregulation, was largely shaped by the experience of inflation in the late 20th century:
-
1960s and 1970s: Milton Friedman predicted inflation in 1967, which began to materialize in the 1970s in countries like Britain and the United States.
-
Institutional Design: Many economic institutions were designed around the goal of maintaining stable prices. When inflation surged, these systems were disrupted.
-
Tax Implications: Non-inflation-adjusted tax rates led to "bracket creep," where inflation pushed individuals into higher tax brackets without real income increases. This fueled the taxpayer revolt movement.
-
Corporate Strategy Shift: High inflation rates made traditional tax breaks for depreciation less valuable, leading many corporations to focus more on financial investments rather than building new factories.
-
Banking Sector Transformation: When Paul Volcker raised interest rates to combat inflation in the early 1980s, it reshaped the banking sector due to statutory limits on interest rates banks could charge.
The Forgetting of Inflation and Its Consequences
As inflation was brought under control, many policymakers and economists began to downplay its importance:
-
Complacency: There was a growing belief that inflation was no longer a significant threat to economic stability.
-
Modern Monetary Theory: Some economists embraced theories suggesting that governments with sovereign currencies could spend freely without worrying about inflation.
-
Policy Shift: Focus shifted away from inflation control towards other economic goals, such as full employment and economic growth.
The Return of Inflation and Its Political Implications
The recent resurgence of inflation has had profound political consequences:
-
Political Realignment: The return of high inflation has contributed to a shift in political attitudes, potentially paving the way for leaders like Donald Trump who promise economic change.
-
Policy Reevaluation: There's a renewed focus on inflation control and its impact on economic policy.
-
Potential for Further Change: The essay suggests that Trump's policies, if implemented, could lead to even higher inflation, which might ultimately undermine his political support.
Milton Friedman's Potential Policy Recommendations
If Milton Friedman were advising policymakers today, he might focus on several key areas:
1. Embracing the Price Mechanism
Friedman consistently advocated for allowing prices to guide economic decisions:
-
Housing Markets: He would likely support removing rent controls and allowing housing prices to be set by market forces.
-
Public Services: For services like national parks, Friedman might suggest funding them through user fees rather than general tax revenue.
2. Reducing Barriers to Entry
Friedman was critical of occupational licensing and other barriers that limit competition:
-
Professional Licensing: He might advocate for reducing licensing requirements in fields where public safety isn't a primary concern.
-
Entrepreneurship: Friedman would likely oppose regulations that create unnecessary barriers for potential entrepreneurs, such as requiring college degrees for certain business activities.
3. Streamlining Government Services
Friedman favored efficient government operations:
-
Negative Income Tax: He proposed implementing a minimum income through the tax system rather than through separate social welfare bureaucracies.
-
Administrative Overhead: Friedman would likely support efforts to reduce administrative costs in government programs.
4. Leveraging Technology
While not available during much of Friedman's career, he would likely support using modern technology to improve government efficiency:
-
Digital Services: Implementing smartphone-based benefit systems and other digital tools to reduce paperwork and speed up service delivery.
-
Real-time Data: Using technology to provide instant pricing signals and economic information to market participants.
5. Monetary Policy
Friedman would likely have strong opinions on current monetary policy:
-
Interest Rates: He might advocate for a more normalized interest rate environment, arguing against prolonged periods of near-zero rates.
-
Inflation Targeting: Friedman would likely stress the importance of maintaining price stability as a primary goal of monetary policy.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing Friedman's ideas in the current political and economic climate would face several challenges:
1. Job Displacement
Streamlining government operations and reducing regulations could lead to job losses, particularly among government employees. This raises important questions about how to balance efficiency with compassion for affected workers.
2. Political Feasibility
Many of Friedman's ideas, such as dramatically reducing occupational licensing or implementing a negative income tax, might face significant political opposition.
3. Technological Implementation
While technology offers opportunities for improving government efficiency, implementing large-scale IT projects in government has historically been challenging and costly.
4. Global Economic Conditions
Friedman's policy prescriptions would need to be adapted to current global economic realities, including the ongoing effects of the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions.
5. Inflation Management
Given the recent resurgence of inflation, policymakers would need to carefully consider how to implement Friedman's ideas without exacerbating inflationary pressures.
Conclusion
Milton Friedman's economic philosophy continues to be relevant in today's political and economic landscape. His emphasis on free markets, price mechanisms, and monetary stability offers valuable insights for addressing current challenges. However, implementing these ideas requires careful consideration of their potential impacts and the need to adapt them to contemporary realities.
As we navigate the complex economic terrain of the 2020s, policymakers and citizens alike would do well to remember Friedman's teachings on the importance of stable prices, free markets, and limited government intervention. At the same time, we must also grapple with the social and political consequences of economic policies, seeking solutions that promote both efficiency and equity in our increasingly interconnected global economy.
Ultimately, the legacy of Milton Friedman reminds us of the importance of studying economic history and maintaining a broad perspective when crafting policy. By learning from past experiences with inflation, government intervention, and market dynamics, we can better prepare for the economic challenges of the future and work towards creating a more prosperous and stable economic environment for all.
Article created from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6z1YA80PyNA