Create articles from any YouTube video or use our API to get YouTube transcriptions
Start for freeUnderstanding Sugar and Its Impact on Health
Sugar, often misunderstood and overconsumed, plays a significant role in various health issues. It's crucial to differentiate between simple sugars and complex carbohydrates, as they impact the body differently. Carbohydrates are composed of sugar, fiber, and starch. However, starch—often overlooked—is essentially long chains of sugar molecules and can significantly spike blood sugar levels.
The Hidden Sugar in Our Diets
When we consume starches found in ultra-processed foods like certain cereals or modified food starches, our blood sugar levels can soar even higher than when consuming simple sugars. For instance, maltodextrin, a common food additive derived from corn, has a glycemic index rating as high as 185 compared to table sugar at 65.
The profitability of products like cornflakes illustrates how inexpensive raw materials like corn can be transformed through processing to generate substantial profits due to their low production costs and high consumer prices.
Top 7 Surprising Signs of Excessive Sugar Consumption
1. Reduced Collagen Production: Excessive sugar intake harms collagen production, leading to premature aging signs like wrinkles and sagging skin.
2. Persistent White Tongue: A chronic white coating on the tongue often indicates an overgrowth of candida—a yeast that thrives on sugar.
3. Chronic Sinus Issues: Many sinus problems are linked to fungal infections that feed on sugar, perpetuating the cycle of infection unless sugar is drastically reduced or eliminated from the diet.
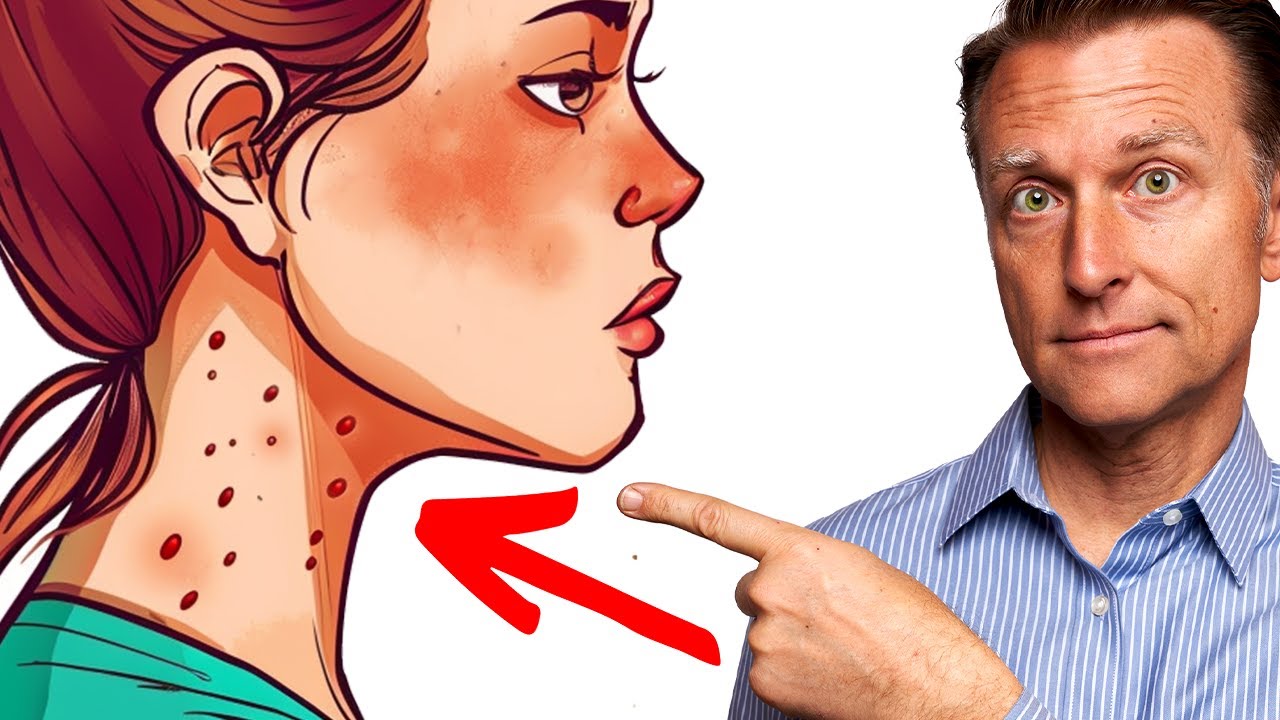
4. Gums Bleeding Easily: Consuming too much sugar can block vitamin C absorption leading to weakened gums—a mild form of scurvy—that bleed during brushing.
5. Low Testosterone Levels: High sugar consumption can lower testosterone levels significantly, affecting libido, muscle building capacity, and overall energy levels.
6. Increased Susceptibility to Infections: A diet high in sugars weakens the immune system making one more prone to infections.
7. Elevated Adrenaline Levels: Surprisingly, excessive sugar intake can lead to increased adrenaline levels not from mental stress but from physical stress at the cellular level due to impaired mitochondrial function.
The Broader Implications of High Sugar Intake
Beyond these direct symptoms linked with excessive sugar consumption lies a broader concern regarding ultra-processed foods' role in public health issues. The economic incentives for producing high-starch foods contribute significantly to their prevalence in diets globally which poses substantial health risks over time.
Understanding these signs and reevaluating our intake can lead not only to better health outcomes but also help mitigate the economic drivers behind processed food production.
Article created from: https://youtu.be/a4zXbFp3djA?si=DVaMAhQlu5SrIuDI


