Create articles from any YouTube video or use our API to get YouTube transcriptions
Start for freeUnderstanding Computer Networks and Their Key Components
Computer networks form the backbone of modern communication, allowing various computing devices to share data seamlessly. At its core, a computer network facilitates the connection between heterogeneous devices, enabling them to share vital information. This connection can be established through various means, including wired and wireless methods, ensuring that data packets move efficiently from the sender to the receiver.
The Role of Senders, Receivers, and Protocols
In any computer network, communication involves a sender and a receiver, which can be machines or users interacting through machines. For successful data transfer, a connection is paramount. However, the mere transfer of data is not enough. Ensuring that the receiver understands the sent data is crucial, which is where protocols come into play. Protocols act as a set of instructions, guiding how data is sent so the receiver can comprehend it. This system ensures that regardless of the language or format, the message is accurately received and understood, facilitating proper communication.
Client-Server Model and Its Significance
Computer networks often operate on a client-server model, where the client sends a request, and the server responds. This model can exist within a single machine or across multiple machines, highlighting the network's versatility. The essence of computer networking shines when clients and servers are physically separate, demonstrating the network's ability to connect devices across vast distances without compromising on the speed or quality of communication.
Achieving Smooth Communication Across Distances
The ultimate goal of a computer network is to make remote communication as smooth and efficient as if the devices were located within the same physical space. This involves creating an environment where devices do not feel the physical separation, a concept made possible through the robust architecture of computer networks. Whether it's accessing a Facebook page or downloading a file, the network ensures fast and reliable data access, mirroring the efficiency of local data retrieval.
Mandatory and Optional Functionalities in Networks
Computer networks utilize a range of functionalities to ensure effective communication. These include mandatory functions like error and flow control, ensuring data integrity and efficient network usage. Optional functionalities, such as encryption and checkpoints, offer additional layers of security and convenience for specific applications, like banking or large file transfers. Understanding these functionalities is crucial for anyone looking to delve deeper into how computer networks operate and are optimized for different needs.
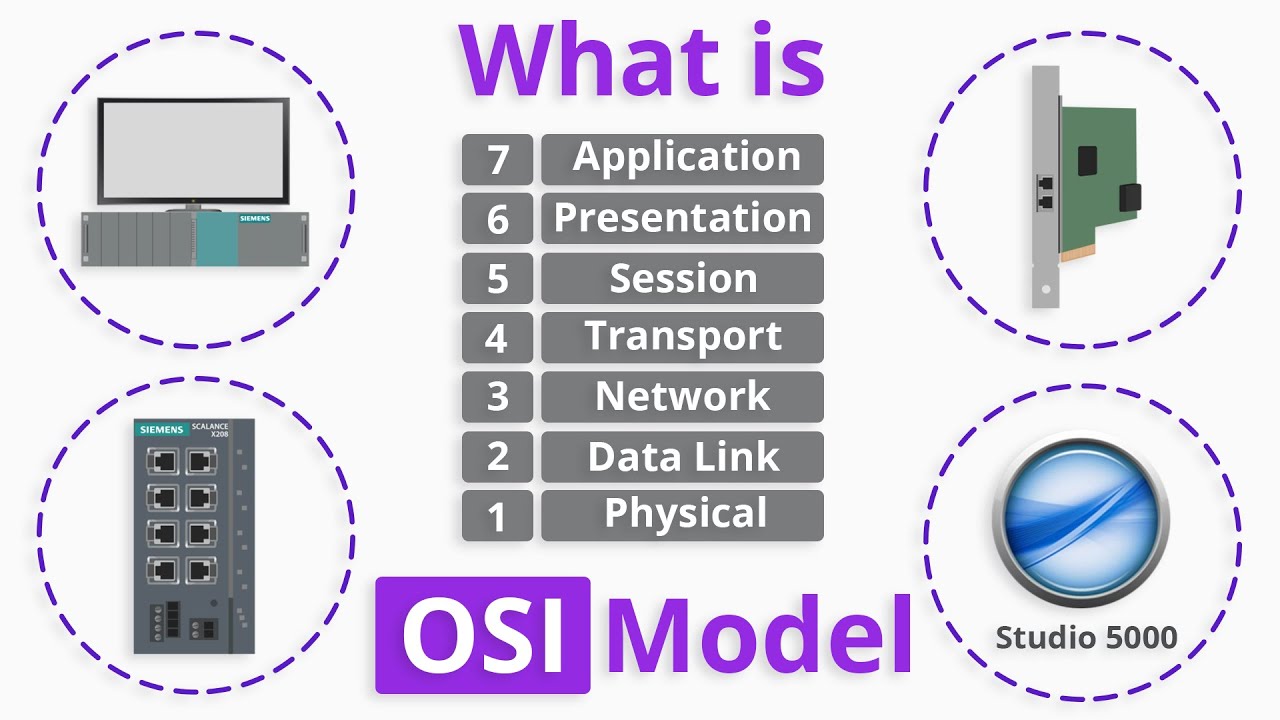
The OSI Model: A Framework for Network Communication
To standardize network communication, functionalities are organized into the OSI (Open System Interconnection) model, which comprises seven layers, each responsible for different aspects of the communication process. This model ensures that data sent from one device is properly processed, transferred, and received by another, adhering to a standardized protocol that guarantees the data's integrity and usability upon receipt.
Conclusion
Computer networks are a fundamental aspect of modern technology, enabling devices to communicate and share data across distances. From establishing connections to implementing protocols and understanding the OSI model, the intricacies of computer networks are vast but essential for the seamless functioning of digital communication. As technology evolves, so too will the complexities and capabilities of computer networks, continuing to bridge the gap between devices no matter their location.
For a deeper dive into the complexities and fundamentals of computer networks, check out the original video here.