Create articles from any YouTube video or use our API to get YouTube transcriptions
Start for freeIntroduction to Flip-Flops in Digital Electronics
The realm of digital electronics is vast and complex, but at its core lies a simple yet powerful component: the flip-flop. Unlike the footwear that shares its name, flip-flops in the world of electronics play a crucial role in the functioning of logic devices. These components are packaged into integrated circuits (ICs) and serve as the building blocks of sequential logic, differentiating themselves from combinational logic devices like multiplexers, demultiplexers, encoders, and decoders.
The Basics of Flip-Flops
Flip-flops, or latches, are categorized as sequential logic devices with a kind of memory that allows them to retain previous data from their inputs or outputs. This characteristic enables them to operate not only based on their current inputs but also on the historical data, making them bistable devices that can exist in one of two states: a logic level 0 or a logic level 1.
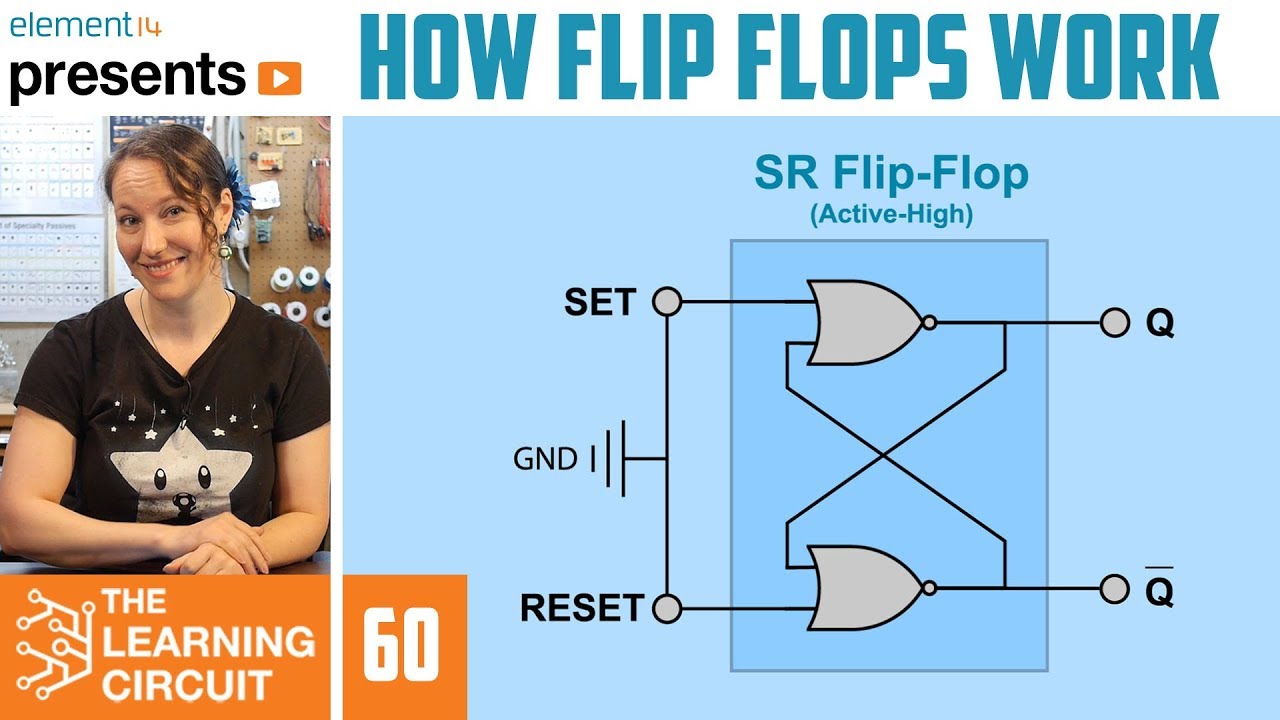
Understanding SR Flip-Flops
One of the simplest forms of sequential logic circuits is the SR flip-flop. It comes with two inputs: one for setting the device (S) and another for resetting it (R). The output, denoted as Q, depends on the state of these inputs, while the second output (not Q or Q̅) is the inverse of Q. This inverse relationship is a fundamental characteristic of flip-flops, where the presence of a circle on the symbol indicates inversion.
Active High vs. Active Low
SR flip-flops can operate in two modes: active high or active low. In an active high configuration, inputs are normally low and become high when activated. The opposite is true for active low circuits, where inputs are typically high and go low when activated. The behavior of the flip-flop changes accordingly, demonstrating the versatility and adaptability of these devices in various circuit designs.
Gated SR Latches
Adding an extra layer of control, gated SR latches incorporate two input AND gates to the set and reset inputs, controlled by a single enable input. This arrangement ensures that the flip-flop responds only when the enable pin is active, providing a higher degree of control over the device's operation.
D Type and JK Flip-Flops
Expanding on the concept of flip-flops, D type and JK flip-flops introduce an additional clock input. This allows the flip-flop to be triggered according to a clock signal, enabling synchronous operation with external timing signals. The clock input acts as an enabler for data inputs, dictating when the data can affect the output state.
The Problem with Set and Reset
While D type flip-flops streamline operations, they can encounter issues if the set and reset inputs are activated simultaneously, leading to an invalid state. This is where JK flip-flops shine, as they eliminate this problem by incorporating feedback mechanisms that prevent such states, ensuring reliable operation.
In Conclusion
Flip-flops are indispensable components in the design of digital circuits, offering memory functionality and sequential logic operation. Whether you're dealing with SR, D type, or JK flip-flops, understanding their principles and applications is crucial for anyone looking to delve into digital electronics.
Your task now is to explore additional inputs like preset and clear, determining how they integrate into the sequential logic of flip-flops. Share your findings and engage with fellow electronics enthusiasts on element14, a community platform for connecting and collaborating with top engineers worldwide.
Happy learning, and remember, the journey into the world of digital electronics is never-ending and always rewarding.