Create articles from any YouTube video or use our API to get YouTube transcriptions
Start for freeUnderstanding Network Protocols and Data Communication
In the realm of computer networks, understanding network protocols and data communication is fundamental. This guide dives in to explain the intricacies of how data is exchanged between nodes, emphasizing the significance of protocols in ensuring efficient communication.
What is Data Communication?
Data communication involves the transfer of data between two nodes via a transmission medium such as cables. This process can occur in different modes:
- Simplex: This is a one-way communication where one node transmits and the other receives. Common examples include keyboards and traditional monitors where information flows only from the device to the CPU.
- Half-Duplex: In this mode, communication occurs in both directions but not simultaneously. Devices like walkie-talkies operate under this mode, allowing one party to speak at a time while others listen.
- Full-Duplex: Unlike half-duplex, full-duplex allows for simultaneous two-way communication. Telephone lines are typical examples where parties can talk and listen at the same time.
The Importance of Protocols in Network Communication
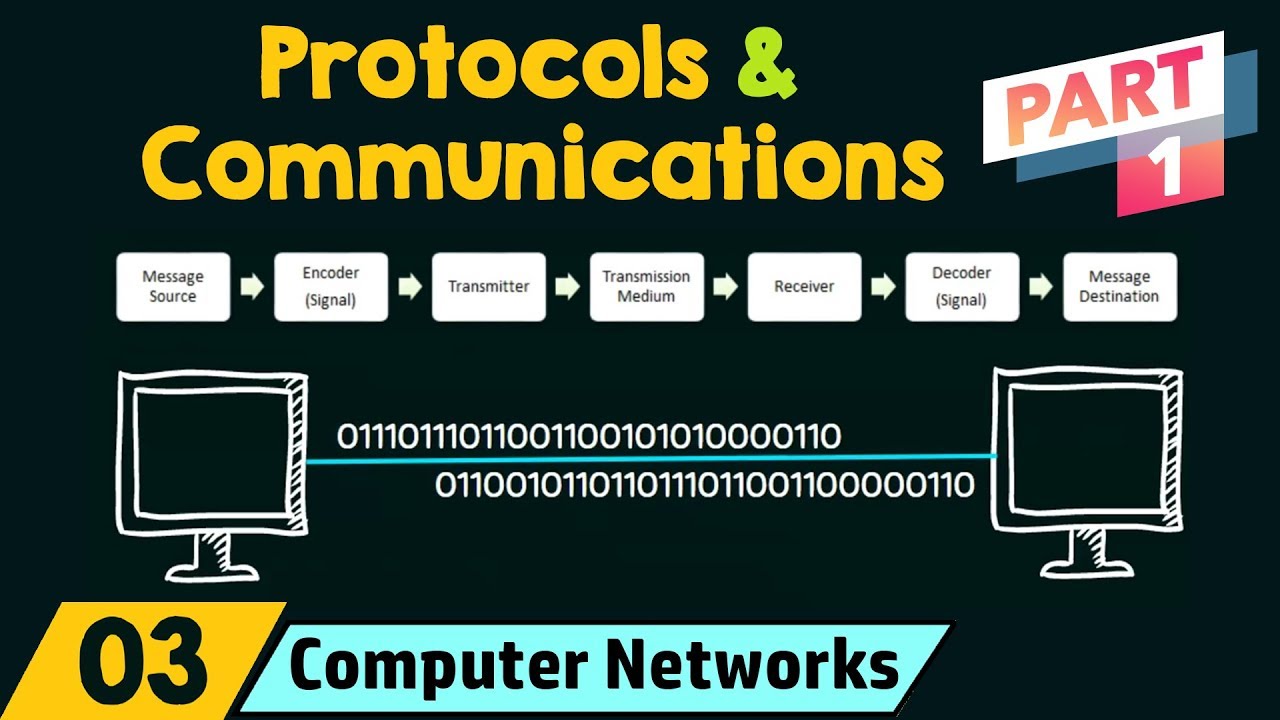
Protocols are sets of rules that govern all forms of communication, whether digital or analog. They ensure that data sent from one point can be understood and processed by another by establishing standards for message encoding, formatting, timing, size, and delivery options.
Key Elements of Protocols:
- Message Encoding: This involves converting data from a source format to a signal that can be transmitted over a chosen medium—wired or wireless.
- Message Formatting and Encapsulation: Data must be packaged or encapsulated with necessary headers or metadata to ensure it reaches the intended recipient correctly formatted.
- Message Sizing: Protocols help break down large messages to match the capacity of the transmission medium which prevents overload and ensures efficient delivery.
- Message Timing: Includes mechanisms like flow control to manage data transfer rates between fast senders and slower receivers ensuring no loss of data occurs due to mismatched speeds.
- Delivery Options: Protocols define whether messages are delivered to single receivers (unicasting), groups (multicasting), or all nodes within a network (broadcasting).
Practical Examples Demonstrating Protocol Use:
- In human communications like speeches or conversations, protocols could involve language choice, speech speed, and feedback mechanisms such as nodding or verbal acknowledgments.
- In digital communications through devices like computers or smartphones using SMS or WhatsApp messages rely on well-defined protocols for successful interaction across diverse networks.
Conclusion:
The seamless exchange of information across computer networks hinges on robust protocols that handle numerous aspects from how messages are sent to how they are received and processed by recipients. By understanding these protocols' roles in both human and network communications we gain insights not only on their functionality but also on their critical importance in maintaining order within systems prone to chaos without these governing rules.
Article created from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ly8ikWtAY7s&list=PLBlnK6fEyqRgMCUAG0XRw78UA8qnv6jEx&index=3


