Create articles from any YouTube video or use our API to get YouTube transcriptions
Start for freeEnhancing Your Understanding of Brain Anatomy
Learning the complex structures of the brain is a fundamental step for students in neuroscience and related fields. Traditional study aids like flashcards and Quizlet are popular tools, but they might not always be effective in providing a thorough understanding of anatomical details. This guide will delve further, offering insights on how to truly master the anatomy of the brain through varied learning approaches.
The Limitations of Flashcards
Flashcards are a staple in many students' study routines. They offer a quick way to review key terms and concepts. However, relying solely on these can be misleading. Students often become familiar with the image or diagram on the card rather than the actual structure it represents. This becomes apparent during exams when the images presented differ from those used in study sessions, leading to confusion and mistakes.
Explorative Learning Techniques
To combat this, it's crucial to engage with materials that challenge your recognition skills beyond static images:
- Interactive Quizzes: Instead of standard flashcards, use interactive quizzes that randomize questions and images to ensure you're not just memorizing layouts.
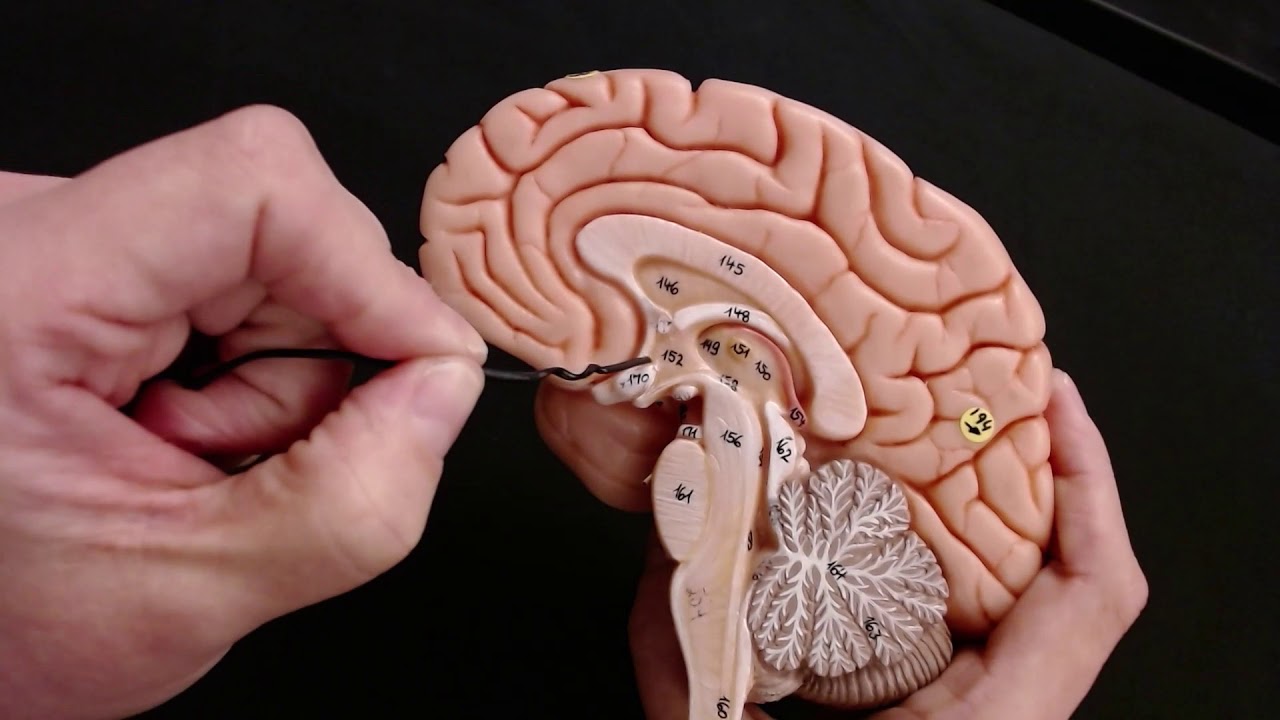
- Anatomical Models: Hands-on practice with 3D models can significantly enhance spatial understanding of brain structures.
- Digital Simulations: Many platforms offer virtual dissections or 3D simulations that provide a more dynamic view of brain anatomy.
Key Brain Regions and Their Functions
Understanding each part of the brain not only involves recognizing it but also knowing its function and relation to other areas:
- Cerebrum: The largest part, responsible for higher cognitive functions such as reasoning, emotions, and speech.
- Cerebellum: Involved in motor control and coordination.
- Brain Stem: Including the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata; it controls basic bodily functions like breathing and heart rate.
- Diencephalon: Houses critical components such as the thalamus and hypothalamus which play roles in sensory information processing and hormonal activity respectively.
Each region is marked by distinct features like gyri (ridges) and sulci (valleys), which are essential for increasing the surface area of the brain.
Study Strategies That Work
To deepen your understanding:
- Mix Up Your Study Tools: Combine flashcards with models, diagrams, and quizzes.
- Teach What You Learn: Explaining concepts to others can help solidify your knowledge and reveal any gaps.
- Change Scenarios: Study different diagrams or models that show structures from various angles or compositions.
- Group Studies: Collaborating with peers can expose you to different interpretations and mnemonic devices.
- Regular Review Sessions: Space out your learning sessions to improve retention over time (spaced repetition).
- Seek Feedback: Don't hesitate to ask for help if certain concepts are challenging; sometimes an external perspective can offer new insights or methods.
- Use Technology Wisely: Leverage apps or online platforms that offer interactive learning experiences tailored to brain anatomy studies.
- Practical Application: Whenever possible, apply your theoretical knowledge through lab work or virtual simulations which mimic real-life scenarios.
- Continuous Learning Curve : Recognize that mastering anatomy is an ongoing process; stay curious about updates in neurological research which might introduce new findings relevant to what you've learned so far.
Article created from: https://youtu.be/yfZQxZhp1zc


