Create articles from any YouTube video or use our API to get YouTube transcriptions
Start for freeUnderstanding the Reversing Valve in Heat Pump Systems
Heat pump systems are versatile heating and cooling solutions that have gained popularity in recent years. At the heart of these systems lies a critical component: the reversing valve. This article will delve into the intricacies of reversing valves, their function, and why they're essential for heat pump operation.
What is a Reversing Valve?
A reversing valve, sometimes referred to as a four-way valve or changeover valve, is a component that allows a heat pump to switch between heating and cooling modes. It's what sets a heat pump apart from a standard air conditioner.
The Role of the Reversing Valve
The primary function of a reversing valve is to redirect the flow of refrigerant within the heat pump system. By doing so, it enables the system to either heat or cool a space, depending on the desired outcome. This flexibility is what makes heat pumps so efficient and versatile.
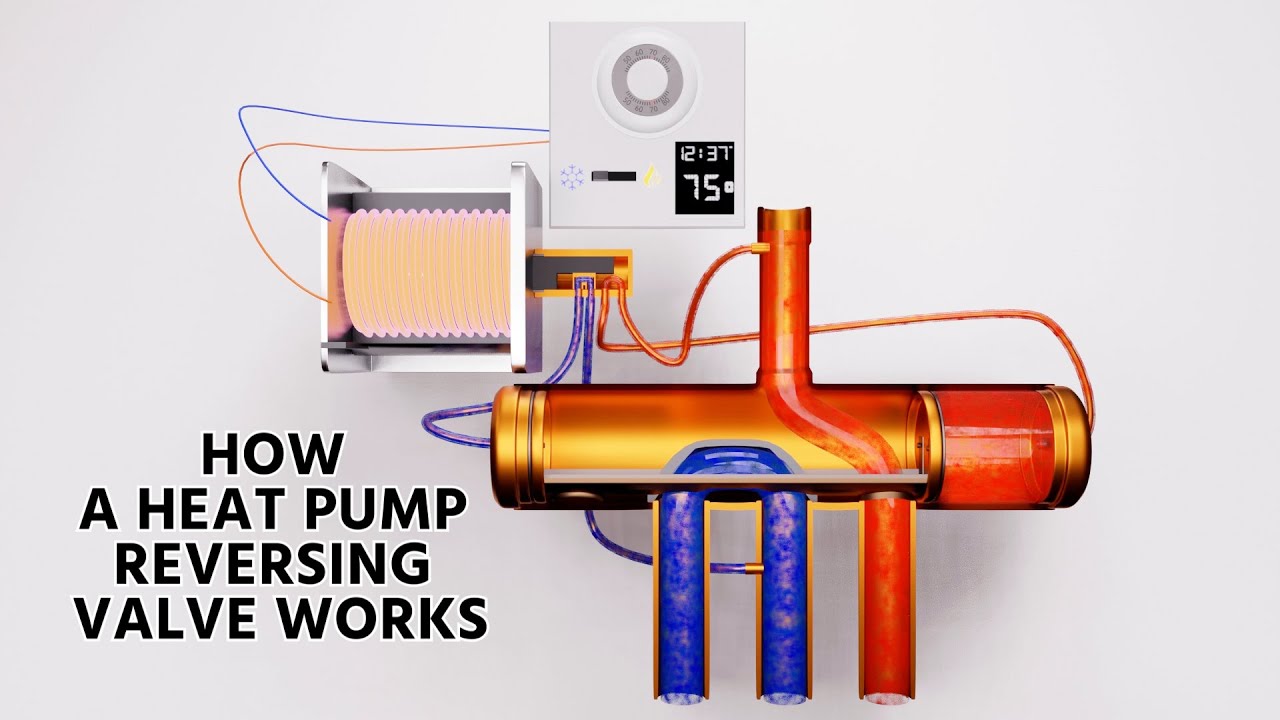
Components of a Reversing Valve
A reversing valve consists of two main parts:
- The Valve Body: This is the physical structure that contains the moving parts and directs the refrigerant flow.
- The Solenoid: An electromagnetic component that initiates the valve's movement.
The Valve Body
The valve body contains several key elements:
- Discharge Line: This is typically the smaller line entering the valve, often located at the top. It's always the discharge line, regardless of the mode of operation.
- Common Suction Line: Located in the center between both sides of the valve, this line is always the suction line.
- Slider: A moving part within the valve that redirects the refrigerant flow.
- Canoe: A small component that helps redirect the suction gas.
The Solenoid
The solenoid is an electromagnetic coil that, when energized, triggers the valve to shift. It's connected to the system's control board and receives signals to change the valve's position.
How a Reversing Valve Works
The operation of a reversing valve is a fascinating process that involves several steps:
- Energizing the Solenoid: When the system needs to switch modes, the solenoid receives an electrical signal.
- Pilot Valve Activation: The energized solenoid activates a small pilot valve within the reversing valve.
- Pressure Differential: The pilot valve creates a pressure differential within the valve body.
- Valve Shift: This pressure difference forces the slider to move, redirecting the refrigerant flow.
Cooling Mode Operation
In cooling mode, the reversing valve directs the hot discharge gas from the compressor to the outdoor coil (acting as the condenser). The cooled refrigerant then flows to the indoor coil (acting as the evaporator), where it absorbs heat from the indoor air.
Heating Mode Operation
In heating mode, the valve shifts, redirecting the hot discharge gas to the indoor coil (now acting as the condenser). The outdoor coil becomes the evaporator, absorbing heat from the outside air.
The Importance of Compressor Pressure
It's crucial to understand that the electromagnetic solenoid doesn't directly move the valve's main slider. Instead, it relies on the pressure created by the compressor. This means:
- The system must be running for the valve to shift.
- If the compressor isn't functioning correctly, the valve may not shift even if the solenoid is energized.
- The valve won't shift when the system is off and pressures are equalized.
Reversing Valve Configurations
There are two main configurations for reversing valves:
- Energized in Cooling: This is the most common configuration. The valve is energized (usually with an orange wire) when the system is in cooling mode.
- Energized in Heating: Some brands, like Ruud and Rheem, use this configuration. The valve is energized (often with a blue wire or B terminal) when the system is in heating mode.
Metering Devices in Heat Pump Systems
In addition to the reversing valve, most heat pumps have two separate metering devices:
- Outdoor Metering Device: Used during heating mode when the outdoor coil is the evaporator.
- Indoor Metering Device: Used during cooling mode when the indoor coil is the evaporator.
These metering devices help regulate the flow of refrigerant, ensuring optimal system performance in both heating and cooling modes.
Troubleshooting Reversing Valve Issues
When a heat pump system isn't switching between heating and cooling modes properly, the reversing valve is often the culprit. Here are some common issues and troubleshooting steps:
Valve Not Shifting
If the valve isn't shifting, check the following:
- Electrical Signal: Ensure the solenoid is receiving the correct voltage.
- Solenoid Functionality: Test the solenoid for continuity.
- Compressor Operation: Verify the compressor is running and creating the necessary pressure differential.
Partial Shift
Sometimes, the valve may partially shift, leading to poor performance. This could be due to:
- Debris in the valve
- Worn internal components
- Insufficient pressure differential
Leaking Valve
A leaking reversing valve can cause the system to lose efficiency or fail to maintain the desired temperature. Signs of a leaking valve include:
- Inconsistent heating or cooling
- Unusual noises from the outdoor unit
- Frost or ice buildup on the refrigerant lines
Maintaining Your Heat Pump System
To ensure your heat pump and its reversing valve continue to function properly, consider the following maintenance tips:
- Regular Inspections: Have a professional HVAC technician inspect your system annually.
- Keep the Outdoor Unit Clean: Remove debris and vegetation from around the outdoor unit.
- Change Filters Regularly: This helps maintain proper airflow and system efficiency.
- Monitor Performance: Pay attention to any changes in heating or cooling performance, as these could indicate reversing valve issues.
The Future of Heat Pump Technology
As heat pump technology continues to advance, we can expect to see improvements in reversing valve design and efficiency. Some potential developments include:
- Smart Reversing Valves: Integration with smart home systems for more precise control and diagnostics.
- Improved Materials: Development of more durable and efficient valve components.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Refinements in valve design to reduce energy loss during the switching process.
Environmental Impact of Heat Pumps
Heat pumps, with their ability to both heat and cool spaces, are increasingly seen as an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional HVAC systems. The reversing valve plays a crucial role in this efficiency:
- Energy Efficiency: By allowing one system to both heat and cool, heat pumps reduce overall energy consumption.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: The ability to extract heat from the air (even in cold temperatures) means less reliance on fossil fuels for heating.
- Longevity: With proper maintenance, heat pumps and their components (including reversing valves) can last for many years, reducing waste.
Choosing the Right Heat Pump System
When selecting a heat pump system for your home or business, consider the following factors:
- Climate: Ensure the system is rated for your local temperature extremes.
- Size: Proper sizing is crucial for efficiency and comfort.
- SEER and HSPF Ratings: Look for high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) ratings.
- Brand Reputation: Choose a manufacturer known for reliability and good customer support.
- Warranty: Check the warranty coverage, especially for major components like the reversing valve and compressor.
Installation Considerations
Proper installation of a heat pump system, including the reversing valve, is crucial for optimal performance:
- Professional Installation: Always have a certified HVAC technician install your heat pump system.
- Proper Refrigerant Charge: Incorrect refrigerant levels can affect the reversing valve's operation.
- Electrical Connections: Ensure all wiring is correct, especially for the reversing valve solenoid.
- System Balancing: The indoor and outdoor units must be properly matched for efficient operation.
Conclusion
The reversing valve is a critical component in heat pump systems, enabling these versatile units to provide both heating and cooling. Understanding how this valve works can help homeowners and technicians alike appreciate the complexity and efficiency of heat pump technology.
As we continue to seek more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly heating and cooling solutions, heat pumps - and by extension, reversing valves - will play an increasingly important role. Whether you're a homeowner looking to upgrade your HVAC system or a technician honing your skills, a solid grasp of reversing valve operation is invaluable.
Remember, while this article provides a comprehensive overview of reversing valves and heat pump systems, it's always best to consult with a certified HVAC professional for specific issues or installations. They can provide tailored advice and ensure your system is operating at peak efficiency, keeping you comfortable year-round while minimizing energy consumption.
Article created from: https://youtu.be/lFV3xT5HCH0?feature=shared


